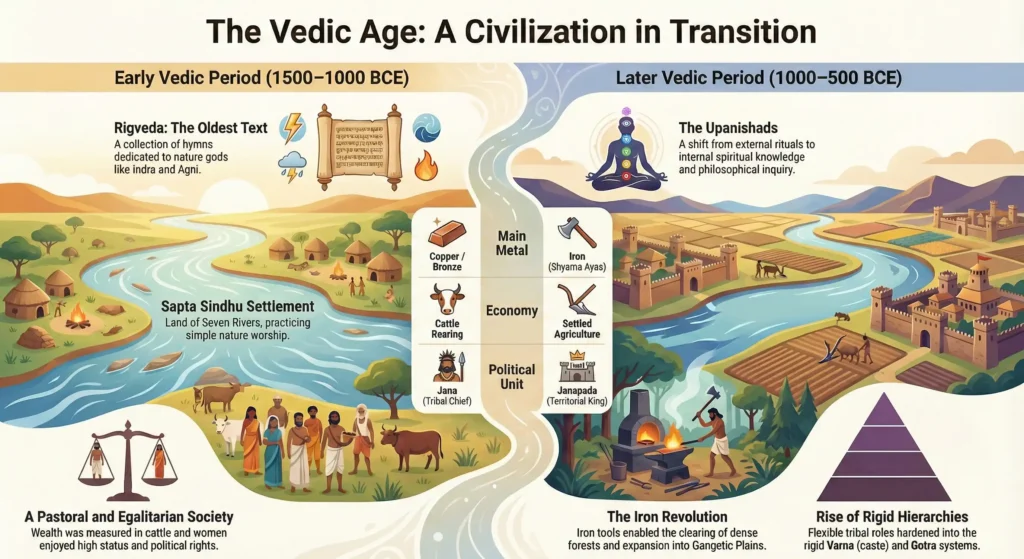
The Vedic Period (c. 1500–500 BCE) is the epoch in Indian history during which the Vedas, the oldest scriptures of Hinduism, were composed. It is broadly divided into two phases: the Early Vedic Period (1500–1000 BCE) and the Later Vedic Period (1000–500 BCE). This era witnessed the migration and settlement of Aryan tribes, initially in the Sapta Sindhu region (Punjab) and later expanding into the Gangetic Plains. The period saw a dramatic transition from a semi-nomadic, pastoral society to a settled, agrarian, and iron-using civilization. It established the social structure of the Varna system (caste), the Sanskrit language, and the philosophical concepts of the Upanishads, setting the stage for the rise of the great Mahajanapadas.| Feature | Details |
| Duration | c. 1500 – 500 BCE |
| Phases | Early Vedic (Rigvedic) & Later Vedic |
| Primary Texts | The Four Vedas (Rig, Sama, Yajur, Atharva) |
| Geography | Indus Valley -> Gangetic Plains |
| Key Metal | Copper/Bronze -> Iron (Shyama Ayas) |
| Economy | Pastoralism -> Agriculture |
| Political Unit | Jana (Tribe) -> Janapada (Kingdom) |
| Pottery | Ochre Coloured Pottery (OCP) -> Painted Grey Ware (PGW) |
The Arrival of the Aryans
Around 1500 BCE, as the Indus Valley Civilization faded, a new group of people entered the subcontinent from the northwest. Calling themselves Aryans (meaning “noble ones”), they spoke an early form of Sanskrit. They settled initially in the Sapta Sindhu (Land of Seven Rivers), encompassing modern Punjab and Haryana.
Rise of Jainism and Buddhism 6th Century BCE
The Four Vedas: The Knowledge
The word “Veda” means knowledge. The literature of this period is the bedrock of Indian philosophy.
- Rigveda: The oldest text, a collection of hymns dedicated to nature gods like Indra and Agni.
- Samaveda: A book of melodies and chants (origins of Indian music).
- Yajurveda: A manual of sacrificial rituals and formulas.
- Atharvaveda: A collection of spells, charms, and medicines for daily life.
Early Vedic Period (1500–1000 BCE)
This was a simple, pastoral age.
- Society: Tribal and egalitarian. The king (Rajan) was a protector of cattle, checked by assemblies like the Sabha and Samiti.
- Economy: Wealth was measured in cows (Gau). Agriculture was secondary.
- Religion: Nature worship prevailed. There were no temples or idols; prayers were offered through fire sacrifices (Yajna).
- Women: Women enjoyed high status, education, and the right to choose husbands.
Later Vedic Period c. 1000-600 BCE: The Age of Iron and Kingdoms
The Iron Revolution (Later Vedic Period: 1000–500 BCE)
Around 1000 BCE, the discovery of Iron (Shyama Ayas) changed history. Iron axes allowed the Aryans to clear the dense forests of the Gangetic plains (modern UP and Bihar), moving the center of civilization eastward.
- Agriculture: Iron ploughshares made deep farming possible. Rice (Vrihi) and Wheat became staples.
- Settled Life: People stopped wandering and settled in territories called Janapadas (foothold of the tribe). The Kuru and Panchala kingdoms rose to power.
Social Stratification: The Varna System
What began as a flexible division of labor in the Early period hardened into a rigid social hierarchy in the Later Vedic period.
- Brahmins: Priests and scholars.
- Kshatriyas: Warriors and rulers.
- Vaishyas: Traders and agriculturists (the tax payers).
- Shudras: Laborers and service providers.The Gotra system (lineage) was established to regulate marriage, and the status of women significantly declined, with them being excluded from political assemblies.
Philosophy: The Upanishads
Towards the end of this period (c. 600 BCE), a reaction against complex rituals began. Sages retreated to forests to compose the Upanishads (Vedanta). They shifted focus from external sacrifice to internal spiritual knowledge (Jnana), discussing concepts like Brahman (Universal Soul) and Atman (Individual Soul), paving the way for Jainism and Buddhism.
Indus Valley Civilization: The Lost Urban Utopia
Quick Comparison Table: Early vs. Later Vedic Period
| Feature | Early Vedic (1500–1000 BCE) | Later Vedic (1000–500 BCE) |
| Geography | Sapta Sindhu (West) | Gangetic Plains (East) |
| Main Occupation | Cattle Rearing | Agriculture |
| Key Metal | Copper/Bronze | Iron |
| King’s Power | Limited (Tribal Chief) | Absolute (Territorial King) |
| Varna System | Flexible (Occupation) | Rigid (Hereditary) |
| Women’s Status | High | Low |
| Main God | Indra, Agni | Prajapati, Vishnu, Rudra |
Curious Indian: Fast Facts
- Satyameva Jayate: India’s national motto comes from the Mundaka Upanishad, composed at the end of this era.
- The Great War: The epic Mahabharata is believed to reflect the dynastic conflicts of the Later Vedic period (specifically the Kuru-Panchala region).
- Archaeology: The Later Vedic period correlates with the Painted Grey Ware (PGW) culture found in archaeological excavations in Hastinapura and Atranjikhera.
- No Salt: The Rigveda does not mention salt or iron, indicating these were discovered or popularized later.
Conclusion
The Vedic Period was the crucible of Indian culture. It gave the subcontinent its primary language (Sanskrit), its social structure (Caste), and its spiritual philosophy (Vedanta). It began with nomadic herders singing to the dawn and ended with powerful kings commanding iron-equipped armies, standing on the threshold of the Second Urbanization.
Early Vedic Period c. 1500-1000 BCE: The Age of the Rigveda
If you think you have remembered everything about this topic take this QUIZ
Results
#1. Which transition in geography characterizes the shift from the Early Vedic to the Later Vedic Period?
#2. In the Early Vedic (Rigvedic) society, how was wealth primarily measured?
#3. Which Veda is known as the ‘Book of Melodies’ and is considered the origin of Indian music?
#4. The discovery of which metal (referred to as ‘Shyama Ayas’) triggered the Second Urbanization and the rise of powerful kingdoms?
#5. How did the status of women change from the Early Vedic period to the Later Vedic period?
#6. What philosophical shift occurred in the ‘Upanishads’ at the end of the Vedic era?
#7. India’s national motto, ‘Satyameva Jayate’, is taken from which ancient Vedic text?
#8. According to the ‘Quick Comparison’ table, who were the main gods of the Early Vedic vs. Later Vedic period?
What is the time period of the Vedic Age?
It spans from approximately 1500 BCE to 500 BCE.
Which is the oldest Veda?
The Rigveda is the oldest.
What metal revolutionized the Later Vedic Period?
Iron (Shyama Ayas or Krishna Ayas).
What are the two main assemblies of the Vedic period?
The Sabha (Council of Elders) and Samiti (General Assembly).
Which region was the center of the Early Vedic civilization?
The Sapta Sindhu (Punjab and surrounding regions).








